Introduction to QR Codes in China
QR codes, or Quick Response codes, were originally developed in 1994 for the automotive industry to track vehicles during manufacturing. However, in recent years, their application has transformed remarkably, especially in China, where they have become ubiquitous. In this digital age, these black-and-white squares play an essential role, extending far beyond mere information retrieval. They are now a fundamental part of daily interactions, payment systems, and social engagement.
The significance of QR codes in China can be attributed to several factors, including the rapid advancement of mobile technology and internet penetration. With over a billion smartphones in circulation, the Chinese populace quickly adapted to this technology, recognizing its convenience and efficiency. Unlike in many other countries, where QR codes have not yet gained widespread acceptance, China has fully embraced them as a modern tool for communication and commerce. As a result, QR codes have become deeply integrated into various aspects of life—from retail transactions to health management systems.
Particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, QR codes became pivotal in facilitating contactless transactions and health monitoring. Citizens were required to scan codes to gain access to public spaces, register for services, and communicate health statuses efficiently. This developed a culture of using QR codes for everyday activities, which further solidified their relevance in Chinese society.
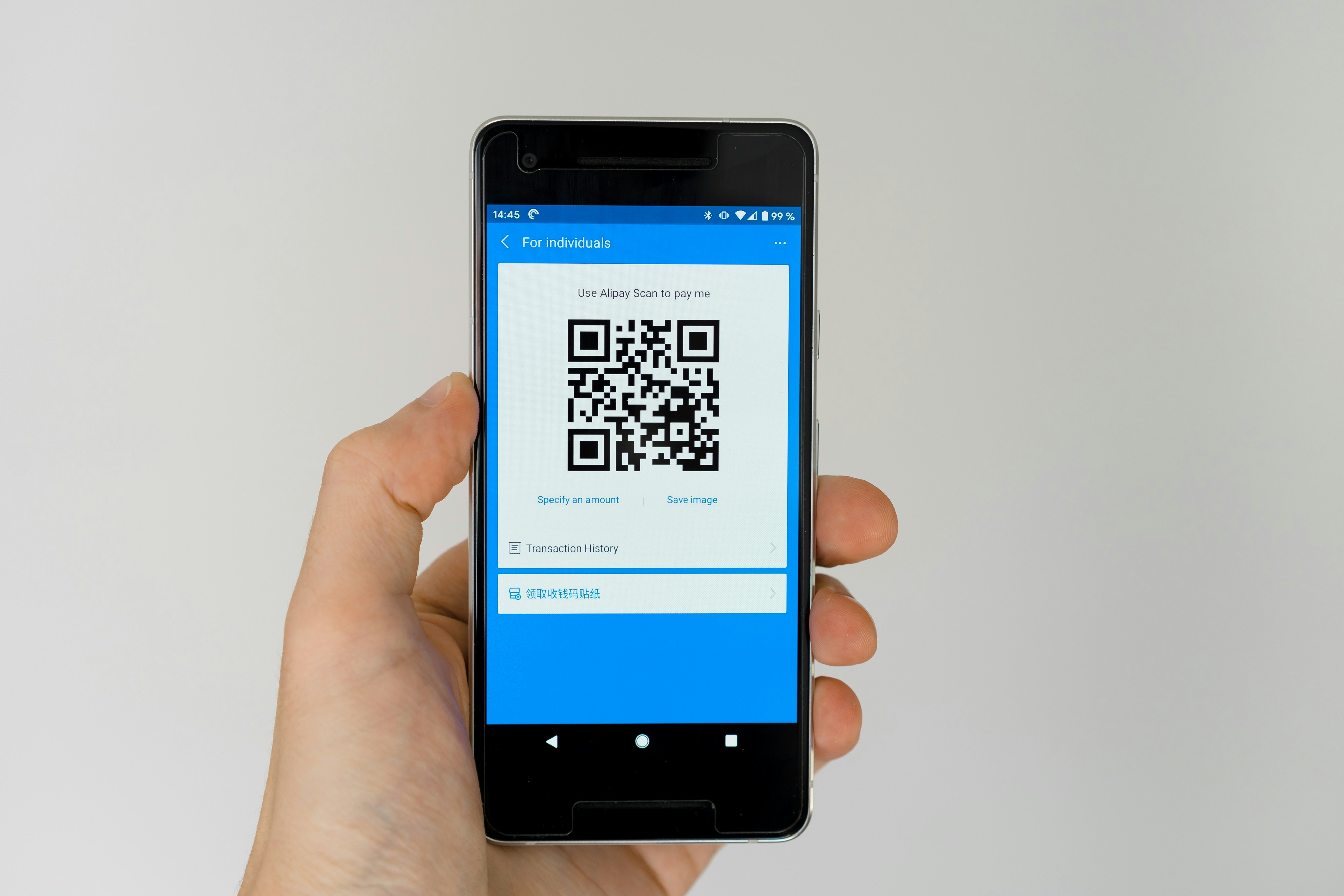
The growth of applications like WeChat and Alipay, which utilize QR codes for payments, has transformed how consumers and businesses interact. By scanning codes, users can make quick payments, access services, or even exchange information seamlessly. As such, QR codes are no longer just a technological novelty; they are a vital element of modern life in China, illustrating a broader trend towards digitization and innovation in the country.
The Rise of Mobile Payment Systems
In recent years, the emergence of mobile payment systems has revolutionized the financial landscape in China, leading to the widespread adoption of QR codes. Platforms such as WeChat Pay and Alipay have become integral in facilitating seamless financial transactions, fostering a cashless society where physical currency is increasingly obsolete. These mobile payment solutions operate effectively through the use of QR codes, which serve as digital keys for consumers and merchants alike.
WeChat Pay, a feature within the widely popular messaging app WeChat, allows users to make payments through simple scanning of QR codes. This convenience has driven substantial adoption across various demographics in China. Similarly, Alipay has distinguished itself as a leader in the mobile payment space, offering a host of services beyond basic transactions, including bill payments, investment options, and consumer loans. With the ability to scan QR codes for instant payments, users can engage in transactions almost effortlessly.
Statistically, the uptake of these platforms has been staggering. In 2022 alone, both WeChat Pay and Alipay accounted for more than 90% of mobile payment transactions in China, signifying a profound shift in consumer behavior. According to recent reports, over 1 billion users are actively engaging with these platforms, showcasing the immense impact QR codes and mobile payments have had on everyday financial practices. The ease of use provided by the integration of QR codes has undoubtedly accelerated this trend, as both consumers and merchants appreciate the speed and efficiency associated with cashless transactions.
This transformation underscores a significant cultural shift in China, as digital wallets continue to gain dominance over cash and credit card usage. The rise of mobile payment systems, facilitated by QR codes, has not only changed the way Chinese consumers manage their finances but has also set a precedent for other regions looking towards a more digitized and efficient payment infrastructure.
QR Codes in Transportation Systems
In recent years, China has witnessed a significant transformation in its transportation systems, largely driven by the widespread adoption of QR codes. This innovative technology has been integrated into a variety of modes of transport, such as trains, buses, and subways, enhancing the overall efficiency and user experience for travelers. With QR codes, travelers can purchase tickets, access travel information, and make payments seamlessly, thus streamlining various aspects of their journeys.
The use of QR codes for train tickets is a prime example of this digital revolution. Gone are the days when passengers were required to wait in long queues for physical tickets. Instead, travelers can now book their train tickets online, receiving a QR code via their mobile devices. This code can be scanned at the station for entry, significantly reducing both waiting time and physical interaction, which is particularly advantageous during peak travel seasons or in situations requiring social distancing.
Similarly, bus payment systems have also adopted QR code technology, allowing passengers to tap their smartphones to pay for their fares. This not only accelerates the boarding process but also minimizes the need for cash transactions, aligning with China’s broader shift towards cashless payments. Furthermore, many cities have introduced QR codes to provide real-time information regarding bus schedules, thereby assisting travelers in planning their trips more effectively.
Overall, the integration of QR codes into China’s transportation systems represents a landmark shift towards modernization and convenience. Travelers benefit from quicker, easier transactions, making public transportation more accessible than ever before. As this digital revolution continues to unfold, it is likely that QR codes will play an increasingly integral role in shaping the future of transportation in China.
E-commerce and QR Codes
QR codes have seamlessly integrated into the e-commerce landscape, transforming how businesses engage with consumers and enhancing the shopping experience. By employing QR codes, retailers can successfully bridge the divide between online and offline shopping, facilitating efficient transactions and customer interaction. For instance, consumers can scan QR codes displayed in physical stores to access detailed product information, reviews, and ultimately streamline their purchasing decisions. This fosters a more informative shopping experience, effectively merging digital engagement with physical retail.
Moreover, QR codes serve as potent tools in marketing strategies, allowing brands to direct potential customers to specific online content effortlessly. Businesses can generate unique codes for promotional materials, print advertisements, and even in-store displays, guiding consumers to special offers, loyalty programs, or even product videos. This approach not only enhances customer engagement but also provides valuable data to retailers, enabling them to track consumer behavior and preferences without intruding upon the user experience.
In China, many high-profile e-commerce platforms, such as Alibaba and JD.com, have capitalized on the use of QR codes to optimize transactions. For example, during major shopping events such as Singles’ Day, QR codes have enabled millions of consumers to access exclusive deals and promotions via their smartphones. This not only improves transaction speed but also streamlines the payment process by linking directly to mobile payment systems, a method widely embraced by Chinese consumers. As a result, QR codes have effectively empowered businesses to create a more dynamic and interactive shopping environment, essential for capturing the interest of today’s consumer.
As e-commerce continues to evolve, it is evident that QR codes will play an increasingly vital role in enhancing marketing strategies, improving customer experience, and driving sales across various retail sectors.
Healthcare Innovations Through QR Codes
The adoption of QR codes in China’s healthcare sector has significantly transformed the way medical services are delivered, improving efficiency and patient experience. One of the primary applications of QR codes is in patient registration. Traditionally, registering a patient often involved lengthy paperwork, which could lead to frustration and delays. With the integration of QR codes, patients are now able to quickly scan a code at healthcare facilities to initiate their registration process. This innovation not only reduces waiting times but also minimizes bureaucratic errors, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care.
Furthermore, the use of QR codes has revolutionized prescription services. In the past, handwritten prescriptions could be misread or misinterpreted, leading to potential issues in medication administration. However, now doctors can create digital prescriptions encoded in QR codes that patients can scan at pharmacies. This system ensures accuracy, enhances medication safety, and simplifies the medication retrieval process. Patients no longer have to worry about losing paper prescriptions, as the codes can be stored digitally on their mobile devices.
Another critical area where QR codes have proven invaluable is in contact tracing during health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. The Chinese government implemented QR code systems that allowed individuals to be tracked based on their movements and potential exposure to the virus. Through a simple scan, authorities could access necessary information to manage outbreaks effectively. This proactive approach exemplified the capability of QR codes in managing public health, mitigating risks, and promoting safety during unprecedented times.
Overall, the incorporation of QR codes in China’s healthcare system illustrates the potential for technology to advance medical services, streamline processes, and ultimately enhance patient care. As QR codes continue to evolve, their utility in various healthcare aspects is poised to expand, paving the way for even more innovations in this vital sector.
Social Integration and QR Codes
In the context of modern social interactions, QR codes have emerged as a pivotal tool that enhances connectivity and engagement among individuals. Initially associated with commercial applications, QR codes have been seamlessly integrated into social networking platforms, enabling users to share contact information, social media profiles, and event details with remarkable ease. This has fundamentally altered how people socialize, facilitating instant connections during gatherings and events.
During community events, such as festivals, exhibitions, and seminars, QR codes serve as a mechanism for attendees to access schedules, program details, and information about exhibitors. Organizers often create promotional materials featuring QR codes that, when scanned, provide users with real-time updates and important announcements. This has allowed for improved engagement among participants, as people can stay informed and connected without relying solely on physical brochures or paper handouts.
Moreover, QR codes have found utility in peer-to-peer interactions. For instance, individuals can generate unique QR codes that link to their online profiles, making it more convenient to exchange information, especially in professional networking contexts. This approach not only streamlines introductions but also fosters a sense of community by encouraging more people to participate actively in social networks. The simplicity of scanning a code also eliminates the awkwardness often associated with traditional methods of sharing contact details.
Furthermore, community programs have adopted QR codes as a means to promote participation and involvement. Initiatives aimed at encouraging locals to join clubs, volunteer organizations, or participate in social activities often employ QR codes in their outreach materials. This strategic integration not only simplifies the registration process but also serves to create a sense of belonging among community members.
Cultural Impact and Public Services
The implementation of QR codes in China has significantly influenced various cultural aspects and transformed the landscape of public services. These two-dimensional barcodes have become a ubiquitous element in daily life, representing a seamless integration of technology into the fabric of society. The adoption of QR codes aligns with China’s push towards modernization and the digital economy, facilitating greater efficiency in public services and enhancing access to information for citizens.
In the realm of government services, QR codes have been instrumental in streamlining processes that were once cumbersome. For instance, citizens can utilize QR codes to access crucial documents, make appointments, and complete transactions with minimal physical interaction. This digital solution has proven especially valuable in rural areas, where technology provides an avenue for government officials to connect with constituents more effectively. Moreover, the convenience afforded by QR codes encourages higher public participation in various services, from taxation to community feedback.
Additionally, QR codes have played a crucial role in public health initiatives, particularly highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic. The use of health QR codes allowed for quick verification of health statuses and travel history, enhancing contact tracing and minimizing virus transmission risks. This technological advancement not only showcased the efficacy of public health measures but also fostered a culture of collective responsibility among citizens. As such, QR codes symbolize modernity in Chinese society, often viewed as a hallmark of progress and innovation.
Overall, the introduction of QR codes has transcended mere functional utility, emerging as a cultural touchstone in China. They signify a leap towards a tech-savvy society where access to government services and public health initiatives becomes increasingly efficient and egalitarian. This evolution reflects the broader societal embrace of digital transformation, placing China at the forefront of technological advancement in the public service sector.
Privacy Concerns and Challenges
The widespread adoption of QR codes in China has raised significant privacy concerns, particularly regarding data security and individual surveillance. As QR codes serve as a gateway to personal information, their implementation prompts a critical examination of how data collected through these codes is stored, shared, and protected. Users often scan QR codes for various services, from payments to health tracking, thus generating vast amounts of data that can potentially be exploited by third parties or government entities.
One of the primary challenges in this digital landscape is ensuring robust data security. Many QR code applications lack stringent security measures, leaving them vulnerable to breaches. This situation can expose sensitive personal information to hackers, raising alarms over how secure users’ data truly is in a QR code-dependent society. Furthermore, with the rapid digitization of services, there is a risk that the urgency of technological advancement may overshadow the necessity for comprehensive privacy regulations. As QR codes proliferate, the demand for stringent standards to regulate their use becomes increasingly essential.
Surveillance is another pressing issue tied to the use of QR codes. Many services, particularly those related to health and travel, utilize QR codes to monitor individuals’ movements and behaviors. While such practices may be justified under the guise of public safety, they can infringe upon personal privacy and freedom. Citizens may face the dilemma of sacrificing some degree of privacy for the convenience that QR codes offer. Therefore, finding the balance between convenience and data protection is vital. The integration of user consent, transparent data usage policies, and effective oversight mechanisms must be prioritized to address these concerns adequately. In this evolving digital environment, fostering trust while harnessing technology is essential for promoting a sustainable QR code ecosystem.
The Future of QR Codes in China and Beyond
The future of QR codes in China appears increasingly promising, with the technology expected to evolve and integrate more deeply into daily life. As a nation that has embraced digital transformation, China is likely to continue leading advancements in QR code applications. One factor driving this trajectory is the growing trend of contactless payments, which has gained momentum amidst the global move towards digital transactions. QR codes facilitate swift and secure payment processes, particularly in a country where credit cards are less commonly used compared to mobile payment systems.
Innovations are anticipated to enhance QR code functionalities. For instance, incorporating augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) could lead to interactive user experiences. Imagine scanning a QR code that not only facilitates a payment but also provides personalized content, discounts, or information tailored to individual preferences. Companies and developers are likely to explore creative integrations that leverage these technologies, making QR codes even more dynamic and engaging.
Furthermore, as the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, the interconnectedness of devices presents vast opportunities for QR codes to become integral in smart environments. For example, smart appliances may incorporate QR codes to allow users to track usage, manage energy consumption, or order supplies seamlessly. This capability strengthens the QR code’s relevance in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
However, challenges exist as well. As QR codes become ubiquitous, concerns regarding security and data privacy are paramount. The potential for malicious actors to exploit QR codes necessitates the development of stringent security measures. Additionally, competition from alternative technologies, such as NFC (Near Field Communication), may arise, influencing the future landscape of digital interactions.
Overall, while QR codes in China are firmly established, their future will rely on continuous innovation and adaptability, determining their role not only in China but also in international digital ecosystems. By embracing both opportunities and challenges, the QR code can evolve to meet the needs of an increasingly digital world.
© barcodly.com- All rights reserved